Ans: Generally, MDPE is viewed as a better option, as it is easier to bend; is resistant to impact; and is also suitable for domestic water pressures.
Is MDPE Better Than HDPE? A Complete Comparison Guide for Modern Piping Projects
Medium-density polyethylene (MDPE) and high-density polyethylene (HDPE) represent two of the most popular piping materials today, each with special benefits regarding performance, durability, and price.
Your selection of one over another will ultimately have an effect on the efficiency and reliability of the project over time, whether the project is gas distribution, water supply, or an industrial application.
MDPE is often considered more flexible as well as stress-crack resistant than HDPE, while HDPE has greater strength and pressure-handling capability. This guide provides comparisons discussing their major differences, merits, and ideal applications for use, enabling engineers, contractors, and project controllers to make informed and future-ready choices in piping material.
Quick Answer – When MDPE Wins and When HDPE Wins
TL;DR: Neither Is “Best” – It Depends on Pressure, Movement & Application
MDPE and HDPE are designed for different performance characteristics, and there is not one material that is universally “better” than another. MDPE is more flexible and offers better impact resistance and slow crack growth resistance making it appropriate for service lines underground and residential water supply connection lines, and local gas distribution lines when soil movement or vibration is more common.
HDPE has better tensile strength and pressure resistance making it appropriate for long distance transmission pipelines, municipal water mains, industrial flow lines, and anywhere pipelines are required to remain under sustained internal pressure and weight over long distances.
Scenarios Where MDPE Is the Smarter Choic
MDPE is the more strategic option in situations where installation routes are irregular, or where pipes need to accommodate bending without frequent joints. They provide a dependable means of mechanical performance for accepting various onsite conditions that occur in urban distribution networks, road crossings, seismic zones, and residential service lines.
They retain better performance under external loads and resistance to slow crack growth. MDPE gives extra safety margin in trenches that are shallow or in urban settings where backfill compaction or traffic vibration may cause stress to the pipe.
Scenarios Where HDPE Is Clearly Better
HDPE is more suitable in high pressure situations or also where running a long, continuous piece of pipe with fewer joints is preferred. Our HDPE is stiffer and allows for better alignment over long distances. Our PE100 has great hoop stress resistance at lower wall thickness. This is why you would typically use HDPE as a main trunk main, for water transmission pipelines, industrial effluent lines, mining slurries, gas transmission systems, etc which utilize higher pressure.
MDPE vs HDPE Basics – What Exactly Are We Comparing?
What Is MDPE (Medium-Density Polyethylene)?
MDPE, or medium-density polyethylene, has a density generally in the range of 0.926 to 0.940 g/cm³. The lower density produces a flexible molecular configuration that allows the polymer to bend easily while remaining crack-resistant to repeated stress.
Because of this balance of ductility and toughness, MDPE is most commonly manufactured as PE80 for pressure-rated service piping. It is primarily used in gas distribution networks, underground potable water service connections, and any situation where the service pipe will be expected to deform under load.
What Is HDPE (High-Density Polyethylene)?
HDPE has a greater density than MDPE which is usually greater than 0.940 g/cm³, higher crystallinity, and higher stiffness, strength, and pressure performance. Current HDPE pressure pipes are commonly manufactured as PE100, which offers significantly greater strength over long periods compared with PE80, while also being able to be thinner-walled for the same pressure rating.
HDPE is often used in large diameter pipelines, heavy industrial systems, high-pressure water mains and in other applications where mechanical stability and continued pressure holding capacity is prioritized above flexibility.
Check out our HDPE Pipe Solutions & Fittings blog to learn more about HDPE pipes, their grades, and their applications.
How Density Links to Strength, Flexibility & Crack Resistance
There is a simple premise involving density relative to impact on performance: increased density translates to increased tensile strength and rigidity, while also reducing flexibility and slow crack growth resistance.
The nature of MDPE’s mechanical structure has lower density, which helps with absorbing impact and resists crack growth more effectively; therefore, it is the preferred option for utilities to use for shallow installations. Conversely, HDPE has a higher density enabling it to properly increase pressure capacity and structural stiffness, providing long-term performance for loaded conditions in more demanding environmental conditions.
Material Grades & Standards – PE80 vs PE100 Explained
What Do PE80 & PE100 Actually Mean?
PE80 and PE100 are Minimum Required Strength (MRS) ratings from long-term hydrostatic testing. PE80 has an MRS value of 8 MPa appropriate for medium-pressure systems. PE100 is rated for minimum required strength of 10 MPa with higher pressure rating using a thinner wall section.
PE100 is a more favorable choice for modern infrastructure projects where long distances and/or pumping pressures must be taken into account to minimize operating costs of the pipeline system over their long service life.
Why MDPE Is Usually PE80 and HDPE Is Often PE100
PE80 and PE100 are stress ratings based on long-term hydrostatic testing referred to as Minimum Required Strength (MRS). PE80 has an MRS value of 8 MPa which is suitable for medium-pressure applications. PE100 is rated to a value of 10 MPa with higher pressure possible using a thinner wall section.
PE100 is a more strategic choice for modern infrastructure projects in which long distances and/or pumping pressures must be considered in order to minimize the pipeline system’s operating costs over a long service life.
Visit this MDPE Pipe Solutions & Fittings blog for installation instructions and technical information on MDPE pipe grades.
Pressure Rating, SDR & How They Affect Pipe Selection
Pipe selection is largely impacted by Standard Dimension Ratio (SDR), which is the pipe’s nominal outer diameter versus wall thickness. For the same SDR, PE100 pipe will withstand greater pressure than a PE80 pipe.
In fact, a PE100 pipe could be rated at the same pressure class as a PE80 pipe, with thinner walls, which lowers pipe weight and material costs. It is the combination of density, grade, and SDR that leads engineers to assess pressure class requirements ahead of selecting a particular material.
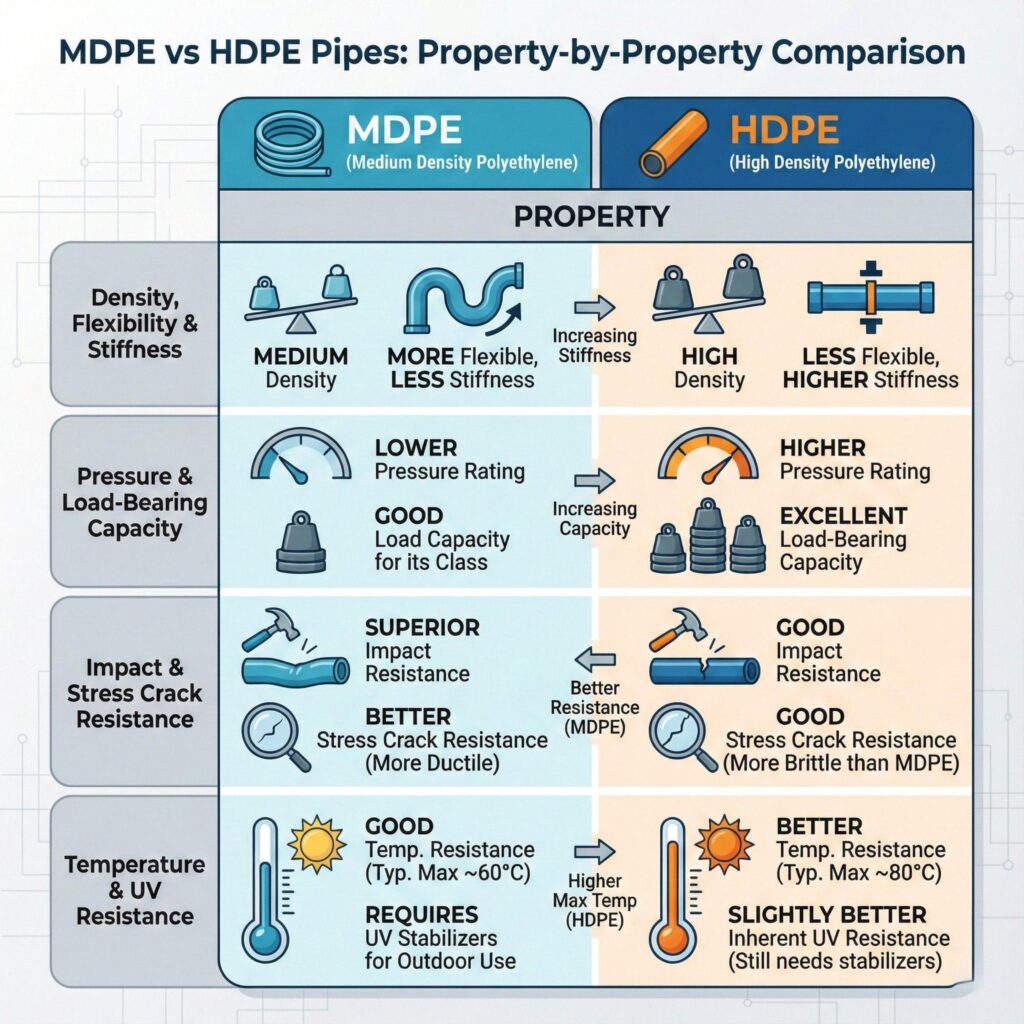
Property-by-Property Comparison: MDPE vs HDPE
Density, Flexibility & Stiffness
MDPE is known for its superior flexibility, enabling easy installation across winding or uneven ground. In contrast, HDPE’s stiffness is more suitable for stability and structure of high-pressure pipelines necessitating alignment across long lengths.
Pressure & Load-Bearing Capacity
HDPE, and particularly PE100, can better withstand higher pressure due to the superior molecular structure found than MDPE. This makes HDPE ideal in pressurized water mains or industrial, and systems need for longer “continuous” level of deformation, risk of is less.
Impact & Stress Crack Resistance
MDPE is more effective at absorbing shocks, and has superior slow crack growth resistance. This performance where the pipe could be impacted during back-filling or soil loads might shift over time.
Temperature & UV Resistance
Both materials have a wide range of temperature resistance, although HDPE is typically more resistant than MDPE. MDPE would perform better, however in cold environments present it behaves better due to its flexibility. With adequate stabilizers both materials would be appropriate for UV resistance in above ground applications.
Read the Difference Between MDPE Pipes and HDPE Pipes blog to understand how different pipe materials perform under extreme conditions.
Application-Wise Comparison – Where Each Material Is Used
Potable Water Supply & Service Connections
MDPE is the material of choice for residential service lines as it bends easily around obstacles, withstands impact during trenching, and is appropriate for the medium pressures that occur in homes and small buildings.
Municipal Water Mains & Long-Distance Pipelines
The strength and pressure class of HDPE/PE100 make it an ideal material for primary water supply networks, long-distance pipelines, and municipal systems with high demand health.
Gas Distribution vs Gas Transmission
Gas utilities typically use MDPE for low-pressure residential gas distribution systems, and HDPE for high pressure transmission lines. MDPE’s flexibility helps to mitigate stress failures in neighborhood gas installations; while HDPE provides additional safety margins for high-pressure gas.
Sewage, Effluent & Industrial Fluids
HDPE is often the preferred material of choice for sewage and industrial lines where a higher strength and rigidity is warranted. MDPE is appropriate in smaller diameter branches on a sewage line, or larger diameter low-pressure effluent lines.
For sewage and wastewater networks, see our Sewage Treatment Plants solutions where to choose the right pipe system.
Residential vs Industrial / Infrastructure Projects
HDPE is often the preferred material of choice for sewage and industrial lines where a higher strength and rigidity is warranted. MDPE is appropriate in smaller diameter branches on a sewage line, or larger diameter low-pressure effluent lines.
Installation, Handling & On-Site Practicality
Trenching, Bending & Handling on Uneven Terrain
The flexibility of MDPE allows it to bend without kinking, meaning fewer fittings, less installation time, and easier re-routing around existing utilities. This is especially helpful for urban retrofits and non-linear trench paths.
Jointing Methods: Electrofusion & Butt Fusion for MDPE and HDPE
Both materials are appropriate for electrofusion and butt fusion to create robust, leakproof connections. HDPE is often butt fused, particularly in larger diameters, when the piping runs are long continuous runs.
Risk of Damage During Backfilling or Ground Movement
MDPE has a high impact strength and is more forgiving from being struck unintentionally by a rock or tool. HDPE is also strong but more rigid, so MDPE is generally safer in locations where soil will be shifting.
Repair, Maintenance & Downtime Considerations
Both materials will have long service lives and little maintenance. If a material is more crack resistant, such as MDPE, repairs will be needed less often in areas with unstable soils. If the material is extremely strong, such as HDPE, normally failures will occur less often in significant high-pressure systems.
Cost, Lifecycle & Performance Over Time
Material & Installation Cost Comparison
Polyethylene (MDPE) generally costs a little less and installs more quickly than HDPE because of its flexibility, resulting in less labor expense to install it. HDPE costs more because of its fabricating material grade and thicker walls for pressure applications, but the added cost is warranted within more stringent installations.
Service Life Expectations
Within Design Parameters) Both MDPE and HDPE will easily get to 50 years plus when properly installed. Their resistance to corrosive products and chemical resistance will cut down on maintenance throughout a lifecycle.
Total Cost of Ownership – When Higher HDPE Cost Is Justified
Higher Cost of HDPE Over MDPE The added cost difference for HDPE is worth the premium when pressure or temperature situations have stricter parameters, or the application is considered ‘industrial’.
Safety, Compliance & Standards
Relevant International & National Standards for MDPE & HDPE Pipes
Both references are founded on international standards that provide a uniform rating at specified pressures, testing and long-term performance characteristics irrespective of geography and suppliers.
Pressure Classes, SDR Ratings & Safety Factors
Safety factors are inherently accounted for under an SDR-based design; HDPE’s capability of achieving even lower SDR’s provided a greater safety factor in high-pressure network constructions.
Regulations for Potable Water, Gas & Sewage Networks
Regulatory organizations will restrict the available materials depending on the network, drinking water, gas networks, sewage etc, and both MDPE and HDPE comply when produced to a recognized standard.
To see how MDPE and HDPE pipes are applied in regulated water and gas systems, visit this Water Management Solutions page
FAQs
Q. Is MDPE or HDPE better for underground domestic water lines?
Q. Can MDPE be used instead of HDPE for high-pressure applications?
Ans: Not typically. High pressure networks almost always will require an HDPE/PE100 solution.
Q. Which material is safer for gas distribution in residential areas?
Ans: MDPE is typically used for low-pressure residential gas distribution, given its crack resistant properties.
Q. Can you mix MDPE and HDPE fittings in the same network?
Ans: They can be accommodated into a network, but transitions must comply with appropriate joining and pressure requirements.







